Post by EchelonHunt on Apr 1, 2016 0:00:59 GMT 8
Metoidioplasty Information:
Metoidioplasty is a FTM sex reassignment surgery procedure developed in the 1970s an alternative to phalloplasty.
Metoidioplasty takes advantage of the testosterone induced growth of the clitoris, and includes lengthening and straightening of the testosterone-enlarged clitoris to create a neophallus, urethral lengthening to enable voiding while standing, and scrotal reconstruction with insertion of testicle prostheses.
It is often performed in one stage.
Metoidioplasty Explained
Metoidioplasty transforms the clitoris into a small penis by releasing it from the hood and cutting the ligament (chordee) that holds the clitoris in place under the pubic bone to allow the entire penile structure to be free of surrounding tissues, giving it more exposure. Additional length of up to 50% can thus be achieved. The labia minora can also be used as flaps to provide tactile protection and additional girth. Additionally, fat can be removed from the pubic mound and the skin pulled up to reposition the penis farther forward (mons resection and phallus repositioning.)
Typical operating time for metoidioplasty procedure is 3-5 hours, and may require additional follow-up procedures and revisions in later stages.
Scrotoplasty and Testicular Implants
To create the scrotum and testicles, the labia majora are dissected, rotated and descended from their original position. Pockets are created in them with incisions to insert testicular implants. Depending on technique and anatomy, the scrotum may have a bifid apperance but this divided scrotum can be joined at a later stage to create a single scrotum with two testicles.
Expanders may be used to stretch the tissues prior to placement of implants. This adds an extra surgery stage but creates a bigger scrotum that can accommodate larger testicular implants.
Urethral Lengthening
Another option with metoidioplasty is urethroplasty or urethral lengthening. Techniques vary (ie. anterior vaginal wall flap vs. buccal mucosa flap) but the results are the same: extension of the urethra from the native urethral opening to the tip of the penis. A catheter is placed inside the new urethra for 2-3 weeks while the body heals. Urethroplasty adds an extra procedure and/or stage, and carries increased risk of urinary complications such as fistula and stricture.
Metoidioplasty results will depend greatly on surgical technique, surgeon experience, anatomy and genital enlargement from testosterone.
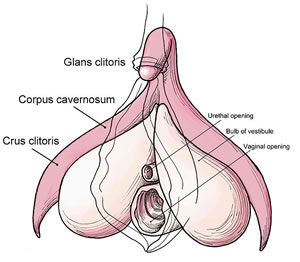

Metoidioplasty Techniques:
Simple Release or Simple Meta
- Clitoral Release
(No Urethroplasty; Vaginectomy and Scrotoplasty with Testicular Implants sometimes performed.)
Ring Metoidioplasty
Partial Vaginectomy
- Clitoral release
- Clitoral lengthening
- Urethroplasty
- Scrotoplasty (optional)
- Testicular implants (optional)
Full Metoidioplasty
- Vaginectomy
- Clitoral release
- Clitoral lengthening
- Urethroplasty
- Scrotoplasty
- Testicular implants
Centurion Metoidioplasty
- Vaginectomy
- Clitoral release
- Clitoral lengthening
- Clitoral girth augmentation
- Urethroplasty
- Scrotoplasty
- Testicular implants
Vaginectomy: An umbrella term referring to surgery procedures that remove all or part of the vagina. The most common vaginectomy performed on FTM transsexuals is colpocleisis, where the vaginal mucosa is removed, the vaginal walls are fused, and the vaginal opening is closed.
Urethroplasty: Extension of the urethra to allow urination while standing.
Scrotoplasty: Creation of testicular sac, with or without implantation of testicular prosthesis.
Mons Resection: Optional procedure that allows the penis and scrotum to be moved to a more forward position and improves access and visibility of the penis by removing excess skin and fat.
PROS: Natal-appearing penis, erotic sensation, unassisted erections, easily concealed scars, shorter operative time, shorter recovery time.
CONS: Small sized penis, good hormonally induced clitoral growth required, typically does not produce a bulge, depending on surgical technique scrotum can have bifid appearance until further revision, urethroplasty may not enable standing to void.
RISKS: Fistula (hole) or stricture (blockage) with urethroplasty, migration and/or extrusion of testicular implants. (There are fewer risks associated with the Simple Meta procedure since urethroplasty is not performed.)
Metoidioplasty Surgeons:
Source: www.metoidioplasty.net/
Phalloplasty Information:
Phalloplasty is a Gender Reassignment Surgery procedure for FTM transsexuals that creates a penis.
Phalloplasty surgery can provide a sensate penis, with erotic and/or tactile sensation, as well as rigidity for sexual intercourse (usually with a penile implant) and the ability to stand to urinate.
Phalloplasty Surgeons construct the penis using a graft of tissue taken from a donor site, such as the forearm, back, leg, abdomen or hip/groin. FTM Phalloplasty may also include vaginectomy, urethroplasty, scrotoplasty, glansplasty and penile implant surgery.
Today's FTM Phalloplasty results are typically exceptional, and have markedly improved in functionality and appearance as the techniques have developed over the past few decades.
(ETA: Phalloplasty is usually performed in 3-4 stages. Dr. Crane has gained reputation for performing 1-2 stage phalloplasty.)
Phalloplasty Techniques:
RFF Phalloplasty:
RFF = Radial Forearm Flap
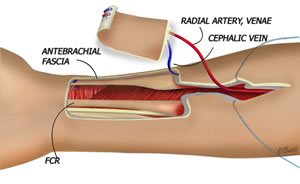
Radial forearm flap is the most common type of FTM phalloplasty. The donor site is thin and supple allowing the flap to be easily tubed and shaped into a penis, and the relatively hairless skin provides erogenous sensation and allows urethral reconstruction in a single stage.
The radial forearm donor site can be closed using a split thickness unmeshed skin graft harvested from the thigh or a full thickness graft from the buttocks.
A Foley catheter is left in place for at least 2 weeks to reduce the risk of stricture and fistula formation while the neo-urethra is healing.
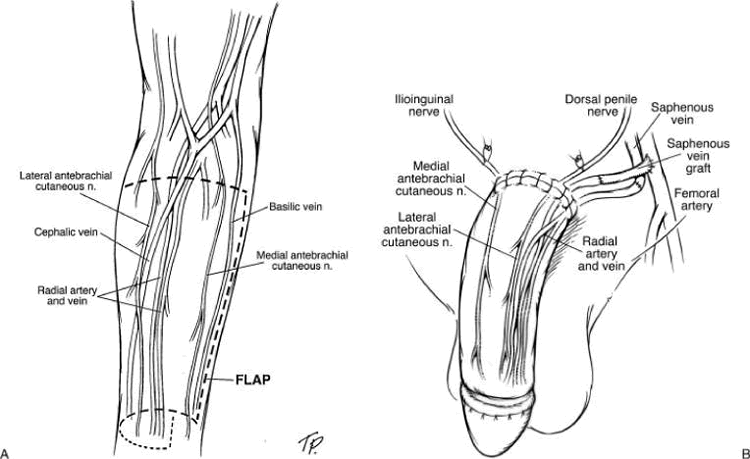
(A) the outline of the radial forearm phalloplasty flap on the arm. The lateral and medial antebrachial cutaneous nerves can be coapted to the ilioinguinal and dorsal penile nerves. The radial artery of the flap can be anastomosed to either the profunda femoris, lateral circumflex femoral, circumflex iliac, or the inferior epigastric artery. The venae comitantes and the cephalic vein of the flap can be anastomosed to branches of the greater saphenous vein. (B) Illustration of the flap following inset, anastomosis, and coaptation. Source: Semin Plast Surg. Aug 2011; 25(3): 196–205.
Aesthetics can be refined with glansplasty: the creation of a corona using a local flap and full thickness skin graft. Tattooing of the corona to match the color of the areola can be done 3 months before sensation returns.
Erectile function can be achieved using a penile prosthesis inserted at a second procedure 10 to 12 months later after tactile sensation has been restored.
Disadvantages: Donor site can be difficult to conceal.
Possible complications: Partial skin graft loss, decreased sensitivity, swelling, less range of hand motion (resolved with hand therapy), decreased grip strength.
ALT Phalloplasty
ALT = Anterolateral Thigh Flap
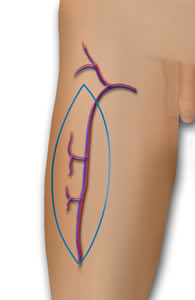
ALT Phalloplasty is a Phalloplasty procedure that uses the thigh donor site to create a sensate and aesthetically satisfactory penis that can be used for sexual intercourse and to void while standing.
The Anterolateral Thigh (ALT) Flap is a skin, fat and fascia flap that has blood supplied by the descending branch of the lateral femoral circumflex vessels and innervation provided by the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve.
While the blood supply of the ALT flap is very good, the layout of the blood vessels can vary, making the surgery complex and tedious.
The thickness of skin and sub-cutaneous fat of the thigh is an important factor in determining if the ALT flap is indicated for Phalloplasty. In the right patient, the ALT flap can be quite thin, making it a good choice for sensation, as well as Stage 1 Urethroplasty.
Patients with thicker skin and more sub-cutaneous fat in the thigh may have excess tissue bulk in the ALT flap that can be a contraindication to Stage 1 Urethroplasty or may not provide aesthetically ideal results. For these patients, Urethroplasty and a debulking procedure can be performed at later stages.
Removing hair from the ALT flap pre-operatively is required. Despite aggressive electrolysis and/or laser hair removal before surgery, some men require additional hair removal post-op, either for urethral issues or cosmetic reasons.
The staging of surgeries with ALT Phalloplasty varies greatly depending on surgeon practices and patient healing, as well as logistics. Most patients can expect to have Vaginectomy, Phalloplasty and Scotoplasty at stage 1. Urethroplasty may be done at stage 1 or stage 2, or is sometimes split over two stages (Primary and Secondary Urethral Lengthening.) Glansplasty can be performed a week after stage 1 with ALT, but is also commonly delayed to stage 2. Implantation of testicular implants is done at stage 2 or 3, and erectile implant is done in the final stage. Urethral repair surgeries and/or cosmetic surgeries may also be incorporated into these stages. In general, one can expect to be fluctuating between surgery and healing stages for up to 2 years post-operatively, and longer if there are complications.
Potential complications early on in the post-operative period can include infection, bleeding, and paresthesia (abnormal sensation from damaged nerves); urethral issues such as fistula and stricture; and partial necrosis or flap loss. Some patients may experience leg weakness or develop adhesions (esp. with pedicled ALT.) Severe complications such as compartment syndrome and muscle necrosis are rare.
The ALT donor site is fairly easily concealed, and operative time is generally less than Radial Forearm Flap Phalloplasty, however sensation is reportedly less than RFF (Monstrey et al., 2008.)
MLD Phalloplasty
MLD = Musculocutaneous Latissimus Dorsi Flap
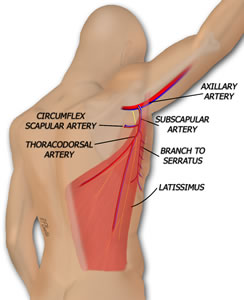
The musculocutaneous* latissimus dorsi (MLD) flap utilizes part of a back muscle and includes the thoracodorsal vessels and nerve. The blood supply is connected to the femoral artery and saphenous vein or the deep inferior epigastric artery and vein, while the nerve is connected to the ilioinguinal nerve.
Only a thin strip of muscle around the pedicle is harvested. The scar is a long, mostly linear scar that runs from under the arm, slightly curved, down to the lower back. In most cases, the donor site can be closed primarily with the incision; sometimes a split thickness skin graft is needed.
This technique yields a penis that is 13-16cm in length and 10-12cm in girth.
Urethroplasty is typically done in two stages: primary urethral lengthening and secondary urethral lengthening. Some surgeons will incorporate a buccal mucosa graft.
Placement of a penile implant can also be done in a later stage. Dr. Vesely from the Czech Republic has described the innervation of the latissimus for erectile function.
Advantages: Low donor site morbidity, easily concealed scar, relatively hairless donor site, good aesthetic outcomes.
Disadvantages: With innervation via a motor nerve, sensation is less than what's typically achieved with RFF phalloplasty (but is usually better than abdominal and groin flap phalloplasty.)
Phalloplasty Surgeons:
Source: www.phallo.net/
Metoidioplasty vs. Phalloplasty
This will be different for everyone as everyone's needs and dysphoria is different.
What may be a pro for you may be a con for someone else, vice versa.
Metoidioplasty:
PROS: Retains original genitalia, unassisted erections, is the cheaper option of the two surgeries, is done in a single surgery, minimal scarring.
CONS: Sexual penetration may not be possible depending on your size, peeing through the fly zipper doesn't always work.
Phalloplasty:
PROS: More aesthetically pleasing penis, can do (assisted) erection/sexual penetration (if you opt for erection implant/device) and urination standing up.
CONS: Scarring of donor sight (forearm, thigh, etc.) may be harrowing to some, surgery is done in 3-4 stages which may not be feasible, lengthy healing process, very expensive to pay out of pocket for unless you live in a place where GRS is covered by health insurance (US) or NHS (UK)
It doesn't matter which option is better than the other, what's important is looking deep within yourself and finding the answer of which surgery you believe will alleviate your dysphoria.
I spent years believing I would go for metoidioplasty because I falsely believed phalloplasty would leave me with zero tactile and erotic sensation, turns out I had been believing misconceptions and once my mind was clear, I knew RFF Phalloplasty is what I need.
Click here for more information - Debunking Phalloplasty Myths
Metoidioplasty is a FTM sex reassignment surgery procedure developed in the 1970s an alternative to phalloplasty.
Metoidioplasty takes advantage of the testosterone induced growth of the clitoris, and includes lengthening and straightening of the testosterone-enlarged clitoris to create a neophallus, urethral lengthening to enable voiding while standing, and scrotal reconstruction with insertion of testicle prostheses.
It is often performed in one stage.
Metoidioplasty Explained
Metoidioplasty transforms the clitoris into a small penis by releasing it from the hood and cutting the ligament (chordee) that holds the clitoris in place under the pubic bone to allow the entire penile structure to be free of surrounding tissues, giving it more exposure. Additional length of up to 50% can thus be achieved. The labia minora can also be used as flaps to provide tactile protection and additional girth. Additionally, fat can be removed from the pubic mound and the skin pulled up to reposition the penis farther forward (mons resection and phallus repositioning.)
Typical operating time for metoidioplasty procedure is 3-5 hours, and may require additional follow-up procedures and revisions in later stages.
Scrotoplasty and Testicular Implants
To create the scrotum and testicles, the labia majora are dissected, rotated and descended from their original position. Pockets are created in them with incisions to insert testicular implants. Depending on technique and anatomy, the scrotum may have a bifid apperance but this divided scrotum can be joined at a later stage to create a single scrotum with two testicles.
Expanders may be used to stretch the tissues prior to placement of implants. This adds an extra surgery stage but creates a bigger scrotum that can accommodate larger testicular implants.
Urethral Lengthening
Another option with metoidioplasty is urethroplasty or urethral lengthening. Techniques vary (ie. anterior vaginal wall flap vs. buccal mucosa flap) but the results are the same: extension of the urethra from the native urethral opening to the tip of the penis. A catheter is placed inside the new urethra for 2-3 weeks while the body heals. Urethroplasty adds an extra procedure and/or stage, and carries increased risk of urinary complications such as fistula and stricture.
Metoidioplasty results will depend greatly on surgical technique, surgeon experience, anatomy and genital enlargement from testosterone.


Metoidioplasty Techniques:
Simple Release or Simple Meta
- Clitoral Release
(No Urethroplasty; Vaginectomy and Scrotoplasty with Testicular Implants sometimes performed.)
Ring Metoidioplasty
Partial Vaginectomy
- Clitoral release
- Clitoral lengthening
- Urethroplasty
- Scrotoplasty (optional)
- Testicular implants (optional)
Full Metoidioplasty
- Vaginectomy
- Clitoral release
- Clitoral lengthening
- Urethroplasty
- Scrotoplasty
- Testicular implants
Centurion Metoidioplasty
- Vaginectomy
- Clitoral release
- Clitoral lengthening
- Clitoral girth augmentation
- Urethroplasty
- Scrotoplasty
- Testicular implants
Vaginectomy: An umbrella term referring to surgery procedures that remove all or part of the vagina. The most common vaginectomy performed on FTM transsexuals is colpocleisis, where the vaginal mucosa is removed, the vaginal walls are fused, and the vaginal opening is closed.
Urethroplasty: Extension of the urethra to allow urination while standing.
Scrotoplasty: Creation of testicular sac, with or without implantation of testicular prosthesis.
Mons Resection: Optional procedure that allows the penis and scrotum to be moved to a more forward position and improves access and visibility of the penis by removing excess skin and fat.
PROS: Natal-appearing penis, erotic sensation, unassisted erections, easily concealed scars, shorter operative time, shorter recovery time.
CONS: Small sized penis, good hormonally induced clitoral growth required, typically does not produce a bulge, depending on surgical technique scrotum can have bifid appearance until further revision, urethroplasty may not enable standing to void.
RISKS: Fistula (hole) or stricture (blockage) with urethroplasty, migration and/or extrusion of testicular implants. (There are fewer risks associated with the Simple Meta procedure since urethroplasty is not performed.)
Metoidioplasty Surgeons:
- Dr. Rumer (US)
- Dr. Dugi (US)
- Dr. Pansritum (TH)
- Dr. Dulin (US)
- Dr. Schechter (US)
- Dr. Melgarejo (MX)
- Dr. Kim (KR)
- Dr. Morel-Journel (FR)
- Dr. Littleton (BR)
- Dr. Mendoza (US)
- Dr. Ferreira (PT)
- Dr. Crane (US)
- Dr. Brassard (CA)
- Dr. Wangjiraniran (TH)
- Dr. Musolas (ES)
- Dr. Mañero (ES)
- Dr. Nguyen (US)
- Dr. Angkatavanich (TH)
- Dr. Tiewtranon (TH)
- Dr. Stasevich (US)
- Dr. Reed (US)
- Dr. Raphael (US)
- Dr. Ralph (UK)
- Dr. Meltzer (US)
- Dr. Medalie (US)
- Dr. McGinn (US)
- Dr. Leis (US)
- Dr. Kanhai (US)
- Dr. Greenwald (US)
- Dr. Djordjevic (RS)
- Dr. Djinovic (RS)
- Dr. Cohanzad (IS)
- Dr. Christopher (UK)
- Dr. Bowers (US)
- Dr. Bouman (US)
- Dr. Belanger (US)
- Dr. Alter (US)
Source: www.metoidioplasty.net/
Phalloplasty Information:
Phalloplasty is a Gender Reassignment Surgery procedure for FTM transsexuals that creates a penis.
Phalloplasty surgery can provide a sensate penis, with erotic and/or tactile sensation, as well as rigidity for sexual intercourse (usually with a penile implant) and the ability to stand to urinate.
Phalloplasty Surgeons construct the penis using a graft of tissue taken from a donor site, such as the forearm, back, leg, abdomen or hip/groin. FTM Phalloplasty may also include vaginectomy, urethroplasty, scrotoplasty, glansplasty and penile implant surgery.
Today's FTM Phalloplasty results are typically exceptional, and have markedly improved in functionality and appearance as the techniques have developed over the past few decades.
(ETA: Phalloplasty is usually performed in 3-4 stages. Dr. Crane has gained reputation for performing 1-2 stage phalloplasty.)
Phalloplasty Techniques:
RFF Phalloplasty:
RFF = Radial Forearm Flap

Radial forearm flap is the most common type of FTM phalloplasty. The donor site is thin and supple allowing the flap to be easily tubed and shaped into a penis, and the relatively hairless skin provides erogenous sensation and allows urethral reconstruction in a single stage.
The radial forearm donor site can be closed using a split thickness unmeshed skin graft harvested from the thigh or a full thickness graft from the buttocks.
A Foley catheter is left in place for at least 2 weeks to reduce the risk of stricture and fistula formation while the neo-urethra is healing.

(A) the outline of the radial forearm phalloplasty flap on the arm. The lateral and medial antebrachial cutaneous nerves can be coapted to the ilioinguinal and dorsal penile nerves. The radial artery of the flap can be anastomosed to either the profunda femoris, lateral circumflex femoral, circumflex iliac, or the inferior epigastric artery. The venae comitantes and the cephalic vein of the flap can be anastomosed to branches of the greater saphenous vein. (B) Illustration of the flap following inset, anastomosis, and coaptation. Source: Semin Plast Surg. Aug 2011; 25(3): 196–205.
Aesthetics can be refined with glansplasty: the creation of a corona using a local flap and full thickness skin graft. Tattooing of the corona to match the color of the areola can be done 3 months before sensation returns.
Erectile function can be achieved using a penile prosthesis inserted at a second procedure 10 to 12 months later after tactile sensation has been restored.
Disadvantages: Donor site can be difficult to conceal.
Possible complications: Partial skin graft loss, decreased sensitivity, swelling, less range of hand motion (resolved with hand therapy), decreased grip strength.
ALT Phalloplasty
ALT = Anterolateral Thigh Flap

ALT Phalloplasty is a Phalloplasty procedure that uses the thigh donor site to create a sensate and aesthetically satisfactory penis that can be used for sexual intercourse and to void while standing.
The Anterolateral Thigh (ALT) Flap is a skin, fat and fascia flap that has blood supplied by the descending branch of the lateral femoral circumflex vessels and innervation provided by the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve.
While the blood supply of the ALT flap is very good, the layout of the blood vessels can vary, making the surgery complex and tedious.
The thickness of skin and sub-cutaneous fat of the thigh is an important factor in determining if the ALT flap is indicated for Phalloplasty. In the right patient, the ALT flap can be quite thin, making it a good choice for sensation, as well as Stage 1 Urethroplasty.
Patients with thicker skin and more sub-cutaneous fat in the thigh may have excess tissue bulk in the ALT flap that can be a contraindication to Stage 1 Urethroplasty or may not provide aesthetically ideal results. For these patients, Urethroplasty and a debulking procedure can be performed at later stages.
Removing hair from the ALT flap pre-operatively is required. Despite aggressive electrolysis and/or laser hair removal before surgery, some men require additional hair removal post-op, either for urethral issues or cosmetic reasons.
The staging of surgeries with ALT Phalloplasty varies greatly depending on surgeon practices and patient healing, as well as logistics. Most patients can expect to have Vaginectomy, Phalloplasty and Scotoplasty at stage 1. Urethroplasty may be done at stage 1 or stage 2, or is sometimes split over two stages (Primary and Secondary Urethral Lengthening.) Glansplasty can be performed a week after stage 1 with ALT, but is also commonly delayed to stage 2. Implantation of testicular implants is done at stage 2 or 3, and erectile implant is done in the final stage. Urethral repair surgeries and/or cosmetic surgeries may also be incorporated into these stages. In general, one can expect to be fluctuating between surgery and healing stages for up to 2 years post-operatively, and longer if there are complications.
Potential complications early on in the post-operative period can include infection, bleeding, and paresthesia (abnormal sensation from damaged nerves); urethral issues such as fistula and stricture; and partial necrosis or flap loss. Some patients may experience leg weakness or develop adhesions (esp. with pedicled ALT.) Severe complications such as compartment syndrome and muscle necrosis are rare.
The ALT donor site is fairly easily concealed, and operative time is generally less than Radial Forearm Flap Phalloplasty, however sensation is reportedly less than RFF (Monstrey et al., 2008.)
MLD Phalloplasty
MLD = Musculocutaneous Latissimus Dorsi Flap

The musculocutaneous* latissimus dorsi (MLD) flap utilizes part of a back muscle and includes the thoracodorsal vessels and nerve. The blood supply is connected to the femoral artery and saphenous vein or the deep inferior epigastric artery and vein, while the nerve is connected to the ilioinguinal nerve.
Only a thin strip of muscle around the pedicle is harvested. The scar is a long, mostly linear scar that runs from under the arm, slightly curved, down to the lower back. In most cases, the donor site can be closed primarily with the incision; sometimes a split thickness skin graft is needed.
This technique yields a penis that is 13-16cm in length and 10-12cm in girth.
Urethroplasty is typically done in two stages: primary urethral lengthening and secondary urethral lengthening. Some surgeons will incorporate a buccal mucosa graft.
Placement of a penile implant can also be done in a later stage. Dr. Vesely from the Czech Republic has described the innervation of the latissimus for erectile function.
Advantages: Low donor site morbidity, easily concealed scar, relatively hairless donor site, good aesthetic outcomes.
Disadvantages: With innervation via a motor nerve, sensation is less than what's typically achieved with RFF phalloplasty (but is usually better than abdominal and groin flap phalloplasty.)
Phalloplasty Surgeons:
- Dr. Kamol (TH)
- Dr. Schechter (US)
- Dr. Crane (US)
- Dr. Chen (US)
- Dr. Salgado (US)
- Dr. Gottlieb (US)
- Dr. McCammon (US)
- Dr. Greenwald (US)
- Dr. Kuzon (US)
- Dr. Monstrey (BE)
- Dr. Ralph (UK)
- Dr. Christopher (UK)
- Dr. Brassard & Dr. Belanger (CA)
- Dr. Bouman & Dr. Buncamper (NL)
- Dr. Daviero (DE)
- Dr. Morel-Journel (FR)
- Dr. Binder & Dr. Desgrandchamps (FR)
- Dr. Mañero (ES)
- Dr. Ferreira (PT)
- Dr. Stasevich (BY)
- Dr. Sukit (TH)
- Dr. Gupta (IN)
- Dr. Chandra (IN)
- Dr. Kaushik (IN)
Source: www.phallo.net/
Metoidioplasty vs. Phalloplasty
This will be different for everyone as everyone's needs and dysphoria is different.
What may be a pro for you may be a con for someone else, vice versa.
Metoidioplasty:
PROS: Retains original genitalia, unassisted erections, is the cheaper option of the two surgeries, is done in a single surgery, minimal scarring.
CONS: Sexual penetration may not be possible depending on your size, peeing through the fly zipper doesn't always work.
Phalloplasty:
PROS: More aesthetically pleasing penis, can do (assisted) erection/sexual penetration (if you opt for erection implant/device) and urination standing up.
CONS: Scarring of donor sight (forearm, thigh, etc.) may be harrowing to some, surgery is done in 3-4 stages which may not be feasible, lengthy healing process, very expensive to pay out of pocket for unless you live in a place where GRS is covered by health insurance (US) or NHS (UK)
It doesn't matter which option is better than the other, what's important is looking deep within yourself and finding the answer of which surgery you believe will alleviate your dysphoria.
I spent years believing I would go for metoidioplasty because I falsely believed phalloplasty would leave me with zero tactile and erotic sensation, turns out I had been believing misconceptions and once my mind was clear, I knew RFF Phalloplasty is what I need.
Click here for more information - Debunking Phalloplasty Myths

